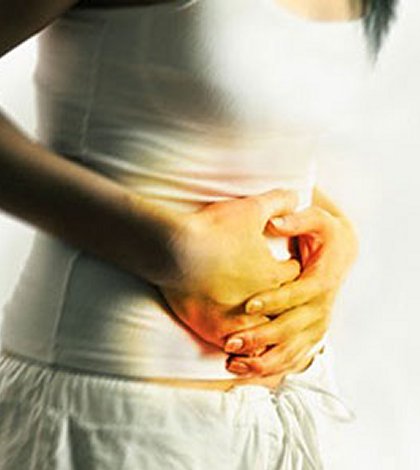
A urinary tract infection can affect one or more parts of the urinary tract from the kidneys to the urethra. This infection is highly treatable with timely diagnosis and proper care.
Symptoms of urinary tract infection are more common in women as their urethra is smaller and closer to the anus (as compared to men). This makes the spreading of germs and bacteria easy, increasing the susceptibility to infection. In men urinary tract infections, though rare, are generally a symptom of some other underlying condition. It is also common in kids below 6 years of age. If the symptoms of a urinary tract infection are not treated well and in time, a simple infection can develop into a severe problem or even a life threatening complication like Sepsis or kidney damage.
It is extremely important to diagnose and treat these bacterial infections in the initial stages to avoid complications. This can be achieved only if the patient consults a doctor when he/she notices the very first symptoms of a urinary tract infection. Though all patients do not develop all the symptoms, there are cases where the infection exists without any noticeable symptoms whatsoever.
Here are some common signs experienced by most patients:
Pain or burning sensation while urinating.
Constant or increased urge to urinate but not much urination (passing of urine).
Feeling that the bladder is full even after urinating.
Discolored, bloody, cloudy or very smelly urine.
More frequent urination, even during the night.
Heaviness of the lower abdomen.
Nausea and vomiting.
Fever and chills.
Flank pain – pain on one side below the ribs where the kidneys are.
In elderly – mental changes or confusion
In men – rectal pain
In women – pelvic pain
In children – Newborns: fever, hypothermia, poor appetite, jaundice; Infants: fever, vomiting, lack of appetite, diarrhea; older children: poor appetite, unexplained fever, loss of bowel control, and change in urination pattern.
Different parts of the urinary tract give rise to different symptoms of urinary tract infection. For example flank or groin pain, fever, nausea is more common when kidney(s ) is/are infected. An infected bladder is more likely to make urination painful and bloody along with pelvic/rectal pain and uneasiness. A burning sensation while urinating is generally associated with the infection of urethra. Many times the symptoms can be confused with those of a sexually transmitted disease (STD). So it is absolutely necessary to consult a doctor.
In most cases, the symptoms of these types of infections go away after a couple days of treatment but this does not indicate the alleviation of the infection. The prescribed course of medication needs to be completed for proper eradication of the infection or it is likely to recur and get severe.
Pregnant women might not get any visible symptoms of urinary tract infection though they are highly susceptible to it. So it is necessary that they are examined for it frequently during their prenatal checkups. A failure to do so might have serious consequences. The infection might spread to the patient’s bloodstream and become life threatening. It can adversely affect the birth weight of the baby and has often been linked to newborn mortality.
Do not neglect even the slightest symptoms if you suspect a health related anomaly.
A urinary tract infection can affect one or more parts of the urinary system. This infection is highly treatable with timely diagnosis and proper care.
However it is extremely important to diagnose and treat these infections in the initial stages to avoid complications. Do not neglect even the slightest symptoms
Adam J Bradley

 Entertainment52 years ago
Entertainment52 years ago
 Entertainment52 years ago
Entertainment52 years ago
 Entertainment52 years ago
Entertainment52 years ago
 Entertainment52 years ago
Entertainment52 years ago